VDK-Service
Introduction
The VDK Service is a runtime environment designed to simplify the development of voice applications. You can integrate it using your preferred language and tech stack, making it ideal for quickly adding voice capabilities to your project.
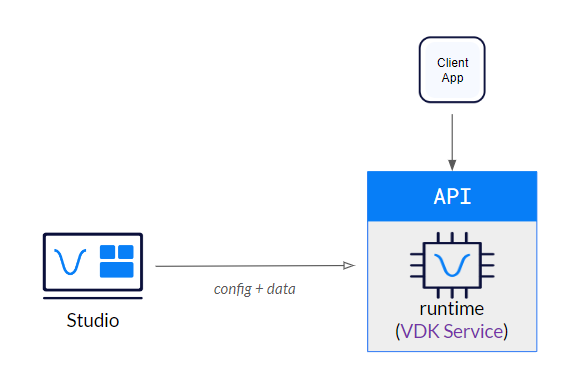
How VDK Service Works
The VDK Service is a binary application that runs locally on your device. It leverages the VSDK (Vivoka Software Development Kit) under the hood to execute the voice commands you send through its API interface.
In practice, this means:
You run the VDK Service binary on your target device.
Your application communicates with it via REST and WebSocket APIs.
The VDK Service then uses VSDK internally to process voice tasks like recognition, synthesis, or enhancement.
This setup allows you to benefit from the power of the VSDK without having to manage its internal components directly.
The VDK Service is built on top of the VSDK, but it may not include all of the features available in the VSDK. We recommend carefully evaluating the benefits of each before deciding which one best fits your needs.
Benefits of using VDK Service
Tech Stack Independance - voice technologies into any tech stack or platform with ease (With VSDK, you're limited to using C++ or Java (for Android) for integration).
Easy Development - voice logic without managing infrastructure or complex dependencies.
Scalability - efficiently to handle growing user traffic.
Request Types
Depending on the route you use, you will encounter different types of requests. Each type requires a specific handling method. Currently, we distinguish only two types: synchronous and asynchronous.
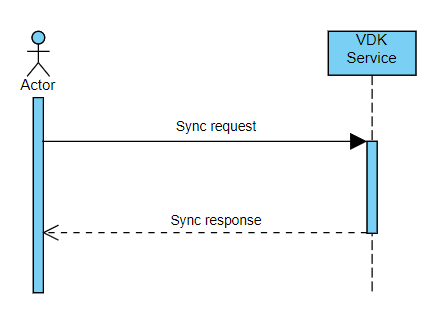
Synchronous Requests
These requests offer a straightforward approach where the client application receives the result directly within the REST API call itself. This is ideal for tasks that require a single, immediate outcome, such as retrieving information or triggering a simple action.
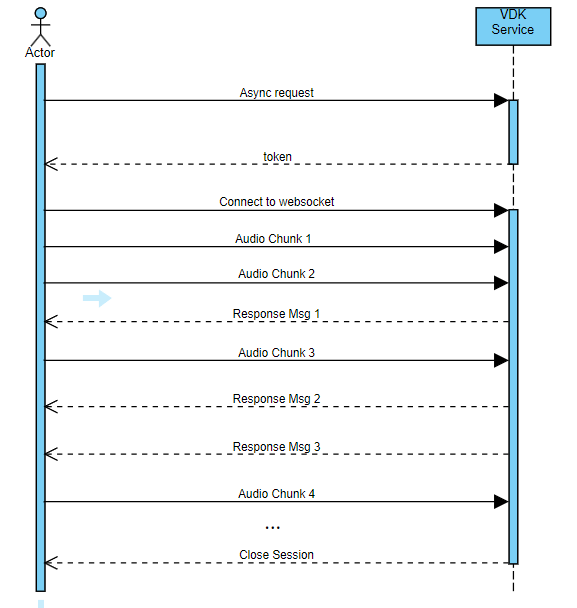
Asynchronous Requests
Asynchronous requests are best suited for scenarios involving continuous data streams or real-time processing. They rely on a WebSocket session, enabling bidirectional, real-time communication between the client and the server. This approach allows for:
Audio Streaming
An audio stream has no clear boundary — systems can’t predict when input will stop or when a result is truly final. Attempting to segment the stream is often tedious and unnecessary, since continuous, adaptive processing naturally handles incoming data as it arrives. This principle underlies technologies like speech recognition and voice enhancement, which refine their output in real time.
Real-Time Processing
Asynchronous communication allows the VDK Service to process the streamed data in real-time, providing results as they become available. This is crucial for applications like speech recognition, where the user receives transcriptions as they speak.
Response Messages
Response types vary depending on the technology used and may include:
Events – Notifications about specific occurrences (e.g., session started, stream ended)
Results – Output data such as recognized text or biometric scores
Errors – Details about processing issues or configuration problems
Processed Audio – Enhanced or modified audio returned after processing (e.g., in speech enhancement)
Where to Go From Here
Depending on stage your are in:
Try VDK Studio – Create and export your first project as a VDK Service.
Run Your Service – Follow the platform-specific setup guide to run the binary on different platforms.
Use the API – Explore available REST and WebSocket endpoints in the API Reference or browse code examples for your language.
